
This documentation is currently under development and subject to change. It reflects outcomes elaborated by 5G-MAG members. If you are interested in becoming a member of the 5G-MAG and actively participating in shaping this work, please contact the Project Office
Scenarios & Use Cases: Content Production and Contribution over Mobile Networks
This section contains information on:
- Reference Scenarios, including:
Single-device Connectivity (Single Camera Live Video Production, Mobile Journalism (MoJo), Newsgathering, Uplink Video)
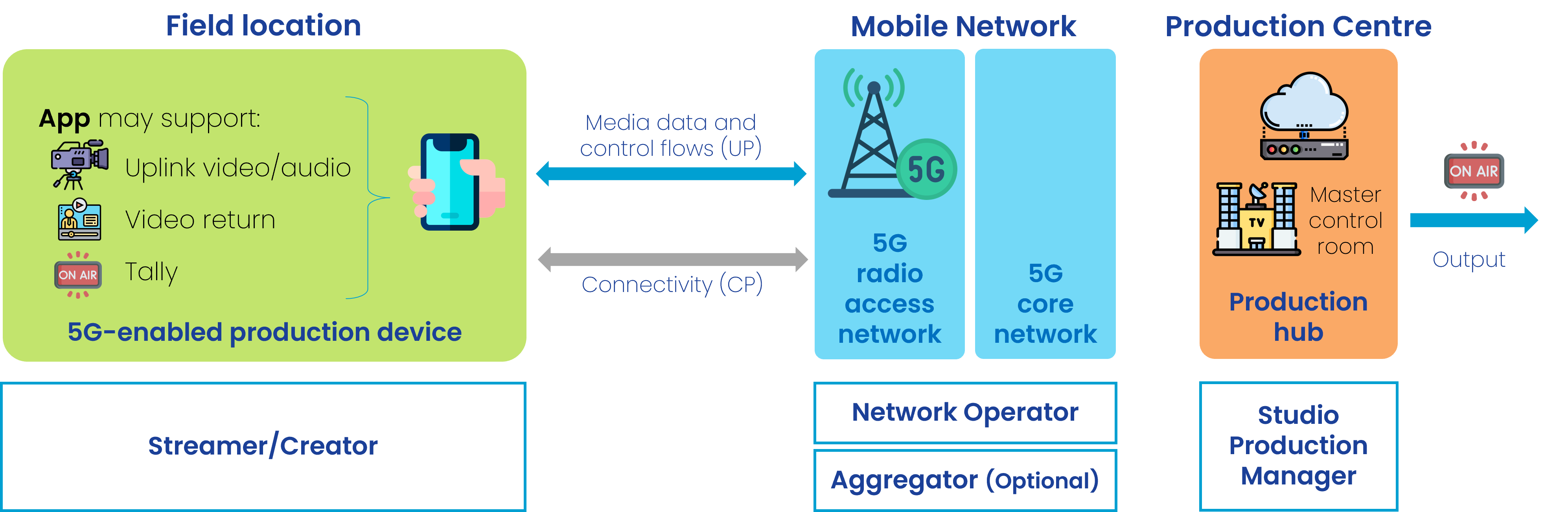
A media producer (e.g. journalist in the field or at a venue) is interested in connectivity for capturing and contributing (uplinking) content to an application server located in the cloud or remote premises. This is a small-size Live Video Production, where practical equipment for immediacy is used e.g. mobile devices (SmartPhones) or camera connected to backpack solutions (specialized devices).
Connectivity with certain quality is required on short notice for one single camera (i.e. uplink video & audio), intercom/remote audio (i.e. speech from the TV Studio), return video (i.e. video from the TV studio), control signals (i.e. tally light).
The following figure represents an scenario where the device is a smartphone.
The following figure represents an scenario where the device is a backpack.
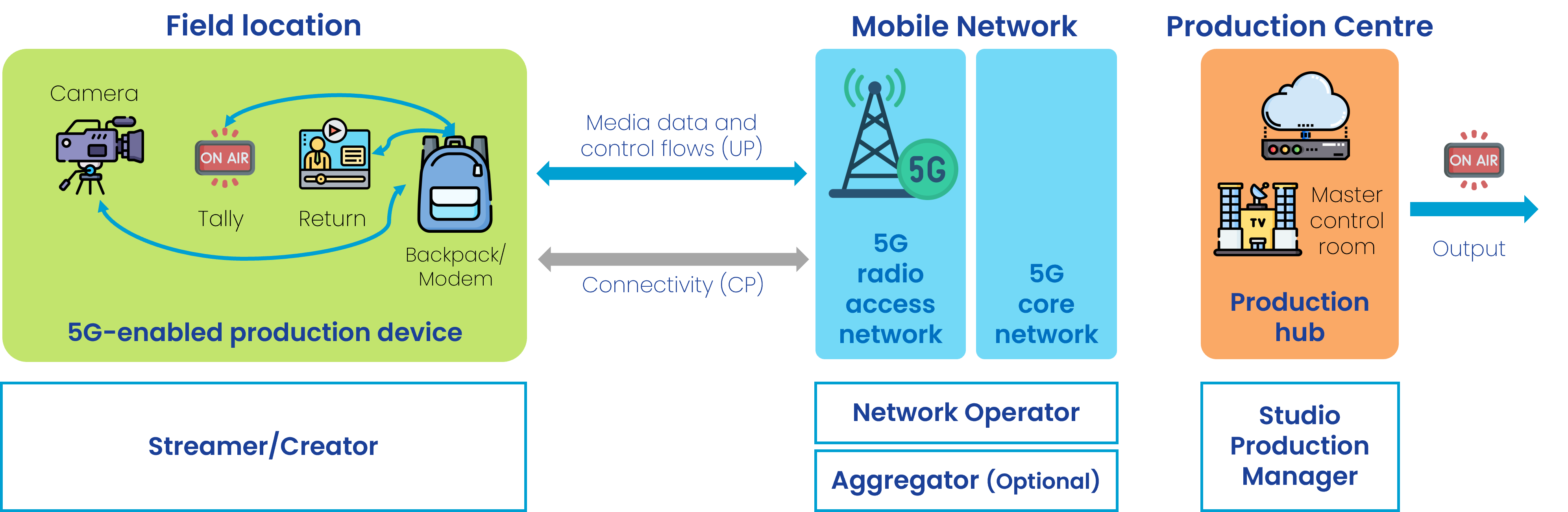
Actors
The actors involved are:
- Streamer/Creator, uses the content acquisition equipment to capture media, uses the network and sends data to the server.
- a Studio Production Manager, located e.g. within the production centre.
- Network Operator, provides the network used for the production. A set of network capabilities can be configured through APIs (referred to as Network APIs in the following).
- Aggregator (optional), provides access to the network capabilties of different Network Operators. See GSMA Open Gateway and GSMA Operator Platform as examples.
Network functions
The network functions and applications involved are:
- Production Device (such as a smartphone or a camera attached which is connected to a modem or a backpack), used by the streamer/creator. The device contains at least one UE with a Subscription (SIM) and can host one or more client applications. A client application can be a video capturing and encoding application, which generates and sends a continuous video stream to a receiving Media Server.
- Network API Platform, used by the Network Operator for exposing network Capabilities. The Network API Platform offers a collection of functions e.g. for Authentication / Authorization of the API Invoker (AuthZ Function) and different API Provider functions for different network capabilities. Beside this, there may be more functions, e.g. for API usage metering, API usage throttling, etc.
- Aggregator API Platform (optional), located in the path between the Network API Platforms and the API Invoker. It grants access to Network API Platforms from different Network Providers.
- API Consumer / Invoker, used by the Production equipment (functions) to interact with the Network API Platform of a Network Provider.
- Media Servers, typically located in the Studio Production Hub (operated by the Production Manager) and interact with the production devices, e.g. receiving video or audio streams.
Multi-device connectivity (Outside Broadcast, Small-Scale Video Production, Remote Production)
A media producer (e.g. production crew deployed in the field or at a venue) is interested in connectivity for covering an event using multiple devices including cameras, audio equipment, intercom, etc. Multiple devices are concurrently used during the production. Not all data flows have the same priority and quality requirements. Therefore, each device and data flow should get the requested connectivity performance (e.g. throughput, latency, jitter,…) and with the desired QoS, which may change for each device and data flow during the production.
Connectivity with certain quality is reserved before the event for the equipment involved.
Two options are considered when it comes to network deployment:
- A network deployed in the field or at a venue that is used to connect devices and manage the production locally. Devices capturing and contributing (uplinking) content deliver it to an application server located in the cloud or in the field location. The final program output may be generated locally and delivered to the production centre using one of the options described in the “newsgathering and mobile journalism” scenario, for instance, by means of a device connected to a mobile network. The scenario may involve the deloyment of different networks:
- An SNPN, deployed locally. Remote connectivity can be provided by means of a fiber connection or a public network (PNI-NPN) to which the SNPN is connected to. However, the networks are detached and traffic from devices is not directly contributed but only the program output.
- A PNI-NPN which provides dedicated connectivity locally and for the production devices.
- A public network to which devices are connected to. Devices are managed remotely and are contributing data to the production centre. In this case, a PNI-NPN may be used to guarantee QoS for the different flows carried across the mobile network.
The following figure represents an scenario involving multiple devices.
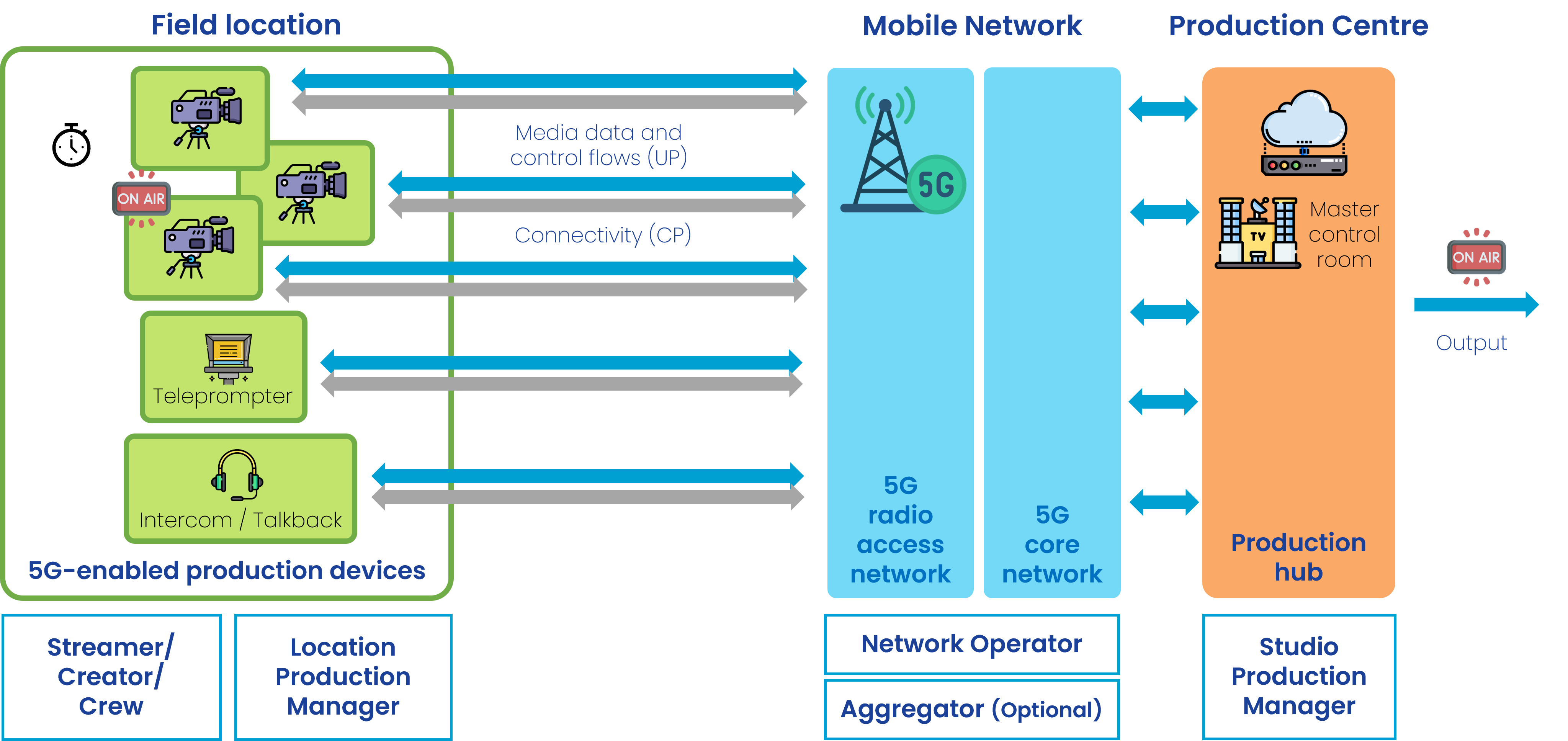
Actors
The actors involved are:
- A Production Manager, deals with the configuration of the production equipment and the access network and has the authority to use the application that interacts with the network operator. It is either:
- a Location Production Manager, who is together with the Production Crew in the field, or
- a Studio Production Manager, who is located e.g. within the production centre.
- Streamer/Creator/Crew, uses the content acquisition equipment to capture media and the network to send data to the server.
- Network Operator, provides the network used for the production. A set of network capabilities can be configured through APIs (referred to as Network APIs in the following).
- Aggregator (optional), provides access to the network capabilties of different Network Operators. See GSMA Open Gateway and GSMA Operator Platform as examples.
Network functions
The network functions and applications involved are:
- Production Devices (such as a Camera), used by the crew during a production. Each device contains at least one UE with a Subscription (SIM) and can host one or more client applications. A client application can be a video capturing and encoding application, which generates and sends a continuous video stream to a receiving Media Server.
- Network API Platform, used by the Network Operator for exposing network Capabilities. The Network API Platform offers a collection of functions e.g. for Authentication / Authorization of the API Invoker (AuthZ Function) and different API Provider functions for different network capabilities. Beside this, there may be more functions, e.g. for API usage metering, API usage throttling, etc.
- Aggregator API Platform (optional), located in the path between the Network API Platforms and the API Invoker. It grants access to Network API Platforms from different Network Providers.
- API Consumer / Invoker, used by the Production equipment (functions) to interact with the Network API Platform of a Network Provider.
- Media Servers, typically located in the Studio Production Hub (operated by the Production Manager) and interact with the production devices, e.g. receiving video or audio streams.
Considerations on Devices
The devices in these scenarios may involve the following:
-
A single UE (e.g. a smartphone or any piece of equipment with a single UE) equipped with a single SIM card (or eSIM) connected to the mobile network.
-
A single device (e.g. a smartphone) equipped with 2 UEs each with 1 SIM card (or eSIM) connected to a different carrier of the same mobile network or different mobile networks. Note that multi-SIM devices enable users to utilize multiple cellular connections simultaneously. Dual-SIM Dual-Active (DSDA) enable this use case with two SIM cards. This is different to Dual-SIM Dual-Standby (DSDS), which allows only one SIM to stay connected with active data at a time. DSDA enhances data performance for end users by enabling the use of two data connections concurrently across SIM1 and SIM2, with the option to choose the best of them or aggregate both, if necessary, to reach higher data throughput.
-
A device with multiple UEs (e.g. a cellular bonding backpack) equipment with multiple SIM cards each one connected to a different carrier of the same mobile network or connected to different mobile networks.